A 19-yr -old army cadet is admitted to hospital with cough, headaches and malaise. He has a temperature of 38°C. His blood count and renal and liver function are normal. Cold agglutinins
are positive. A CXR shows bibasal shadowing.
What is the most likely Dx?
A. Legionella pneumonia
B. Viral pneumonia
C. Q fever
D. Klebsiella pneumonia
E. Mycoplasma pneumonia
Answer:
Study and Memorize Medical Conditions With The Help Of Photos. Useful Site For Medical Students, Doctors And Nurses.
Wednesday, February 1, 2017
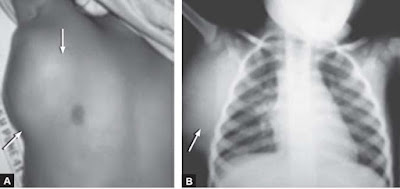
A 3 Year Old Child With A Mass On The Chest
A 3 years old child was seen by the pediatrician for a large soft tissue mass on right side of chest.
Photograph (A) of the child shows the soft mass (arrow), on X-ray chest (B) the soft tissue lymph nodal mass lies outside the thoracic cage in right hemithorax.
Diagnosis: Lymph node mass.
Discussion: On X-ray chest the lung fields are clear, on X-ray chest it is important to look for any lesion in the soft tissue over the entire available film. It may be in the form of enlarged thyroid gland, cervical or axillary lymph nodes, neurofibroma, surgical emphysema, a lesion in the breast or one
of the breasts might have been surgically excised. Ultrasound can be useful in investigating nodal masses particularly as an aid to biopsy.
Photograph (A) of the child shows the soft mass (arrow), on X-ray chest (B) the soft tissue lymph nodal mass lies outside the thoracic cage in right hemithorax.
Diagnosis: Lymph node mass.
Discussion: On X-ray chest the lung fields are clear, on X-ray chest it is important to look for any lesion in the soft tissue over the entire available film. It may be in the form of enlarged thyroid gland, cervical or axillary lymph nodes, neurofibroma, surgical emphysema, a lesion in the breast or one
of the breasts might have been surgically excised. Ultrasound can be useful in investigating nodal masses particularly as an aid to biopsy.
Acromioclavicular Joint Seperation
Injury to the acromioclavicular (AC) joint usually results from an impact on the superior aspect of the acromion.
The classification system for AC joint injuries includes six types.
Clinical Features: Patients complain of pain at the AC joint and will actively splint the injured shoulder. Ecchymosis may be present; however, an obvious deformity is not always seen. There is significant tenderness upon palpation of the AC joint.
Diagnosis: Standard radiographs should include anteroposterior (AP) and axillary lateral views of the shoulder.
The classification system for AC joint injuries includes six types.
- A type I injury is equivalent to a stretching of the AC ligament.
- A type II injury consists of tearing of the AC ligaments and stretching of the coracoclavicular ligaments.
- Complete disruption of the AC and coracoclavicular ligaments is seen in types III to VI.
Clinical Features: Patients complain of pain at the AC joint and will actively splint the injured shoulder. Ecchymosis may be present; however, an obvious deformity is not always seen. There is significant tenderness upon palpation of the AC joint.
Diagnosis: Standard radiographs should include anteroposterior (AP) and axillary lateral views of the shoulder.
Testicular Torsion
A young male , age 16 years presents to the emergency with the complain of the sudden onset of pain in one testicle, followed by swelling of the affected testicle, reddening of the overlying scrotal skin, lower abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting.
An examination reveals a swollen, tender, retracted testicle that often lies in the horizontal plane (bell-clapper deformity).
A diagnosis of Testicular torsion was made and the patient was prepared for immediate surgery.
Case Discussion:
Testicular torsion is one of the urologic emergencies and is very painful on presentation.
Testicular torsion occurs when a testicle rotates, twisting the spermatic cord that brings blood to the scrotum. The reduced blood flow causes sudden and often severe pain and swelling.
Testicular torsion is most common between ages 12 and 16, but it can occur at any age, even before birth.
An examination reveals a swollen, tender, retracted testicle that often lies in the horizontal plane (bell-clapper deformity).
A diagnosis of Testicular torsion was made and the patient was prepared for immediate surgery.
Case Discussion:
Testicular torsion is one of the urologic emergencies and is very painful on presentation.
Testicular torsion occurs when a testicle rotates, twisting the spermatic cord that brings blood to the scrotum. The reduced blood flow causes sudden and often severe pain and swelling.
Testicular torsion is most common between ages 12 and 16, but it can occur at any age, even before birth.
Traumatic Asphyxia - Brief Discussion
Traumatic Asphyxia: Traumatic asphyxia, also known as Perthe's syndrome, is a medical emergency caused by an intense compression of the thoracic cavity, causing venous back-flow from the right side of the heart into the veins of the neck and the brain
The clinical findings of traumatic asphyxia are due to a sudden increase in intrathoracic pressure against a closed glottis. The elevated pressure is transmitted to the veins, venules, and capillaries of the head, neck, extremities, and upper torso, resulting in capillary rupture.
Strangulation and hanging are common mechanisms. Survivors demonstrate plethora, ecchymoses, petechiae, and subconjunctival and retinal hemorrhages.
Body showing dark purple Tardieu spots in dependent areas, due to ruptured capillaries in a person who suffered from Traumatic Asphayxia
Severe injuries may produce central nervous system injury with blindness, seizures, posturing, and paraplegia and even death.
Management: Treatment is supportive, with attention to other concurrent injuries. Long-term
The clinical findings of traumatic asphyxia are due to a sudden increase in intrathoracic pressure against a closed glottis. The elevated pressure is transmitted to the veins, venules, and capillaries of the head, neck, extremities, and upper torso, resulting in capillary rupture.
Strangulation and hanging are common mechanisms. Survivors demonstrate plethora, ecchymoses, petechiae, and subconjunctival and retinal hemorrhages.
Body showing dark purple Tardieu spots in dependent areas, due to ruptured capillaries in a person who suffered from Traumatic Asphayxia
Severe injuries may produce central nervous system injury with blindness, seizures, posturing, and paraplegia and even death.
Management: Treatment is supportive, with attention to other concurrent injuries. Long-term
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)